Biotherapeutics and advanced therapies


IFPMA spotlights how the innovative pharmaceutical industry is delivering a new generation of treatments while explaining the science-based regulatory requirements needed to make sure they deliver maximum therapeutic impact.
Overview
Biotherapeutic medicines benefit more than 350 million patients worldwide, treating widespread diseases such as cancer and diabetes, as well as rare illnesses.
Over the past 30 years, medical advances in biotherapeutic medicines have focused on treating many complex chronic diseases – including cancer, diabetes, hepatitis C, and chronic renal failure – as well as less common ones such as hemophilia, Fabry’s disease, growth deficiency, multiple sclerosis, and Crohn’s disease.
Biotherapeutics
Produced from harnessing and modifying living cells to make or partially change protein products to create therapies, biotherapeutics open new avenues for delivering leading edge treatments for numerous diseases and wide patient populations.
Biotherapeutics have proven to be effective in using chemically synthesized small molecule medicines to treat some particularly difficult conditions.

As with all medicines, the research and development process for biotherapeutics involves a high degree of scientific and economic risk, so there’s a need for strong intellectual property rights to incentivize innovation.
How biotherapeutics are made
Making biotherapeutics is a complex process. The most effective cell line is selected to be expanded, grown in bioreactors, and monitored carefully. This process requires highly sophisticated production, control, and regulatory processes to ensure quality, safety, and efficacy.
Modern biotechnology techniques introduced in recent years have greatly enhanced the ability to develop biotherapeutics safely and consistently.
When developing biotherapeutics, years of research focus on finding the right organism and manufacturing conditions to produce the required protein or antibody. To make sure they are high quality, safe and effective demands precision and conformance to scientific requirements. A small change in the manufacturing process can affect the final product. Scientists must create the right environment for cells to isolate and purify the biotherapeutic protein so it’s exactly the right product every time.
Biotherapeutics require specific regulatory frameworks to control how they are developed, manufactured, used in clinical practice, and approved by National Regulatory Authorities (NRAs).
The manufacturing process must be tightly controlled for consistent quality. Rigorous clinical studies to demonstrate safety and efficacy must be carried out in patients. The safety and efficacy of all biotherapeutics must undergo post-approval monitoring using data comping from real-world clinical practice.
Biosimilars
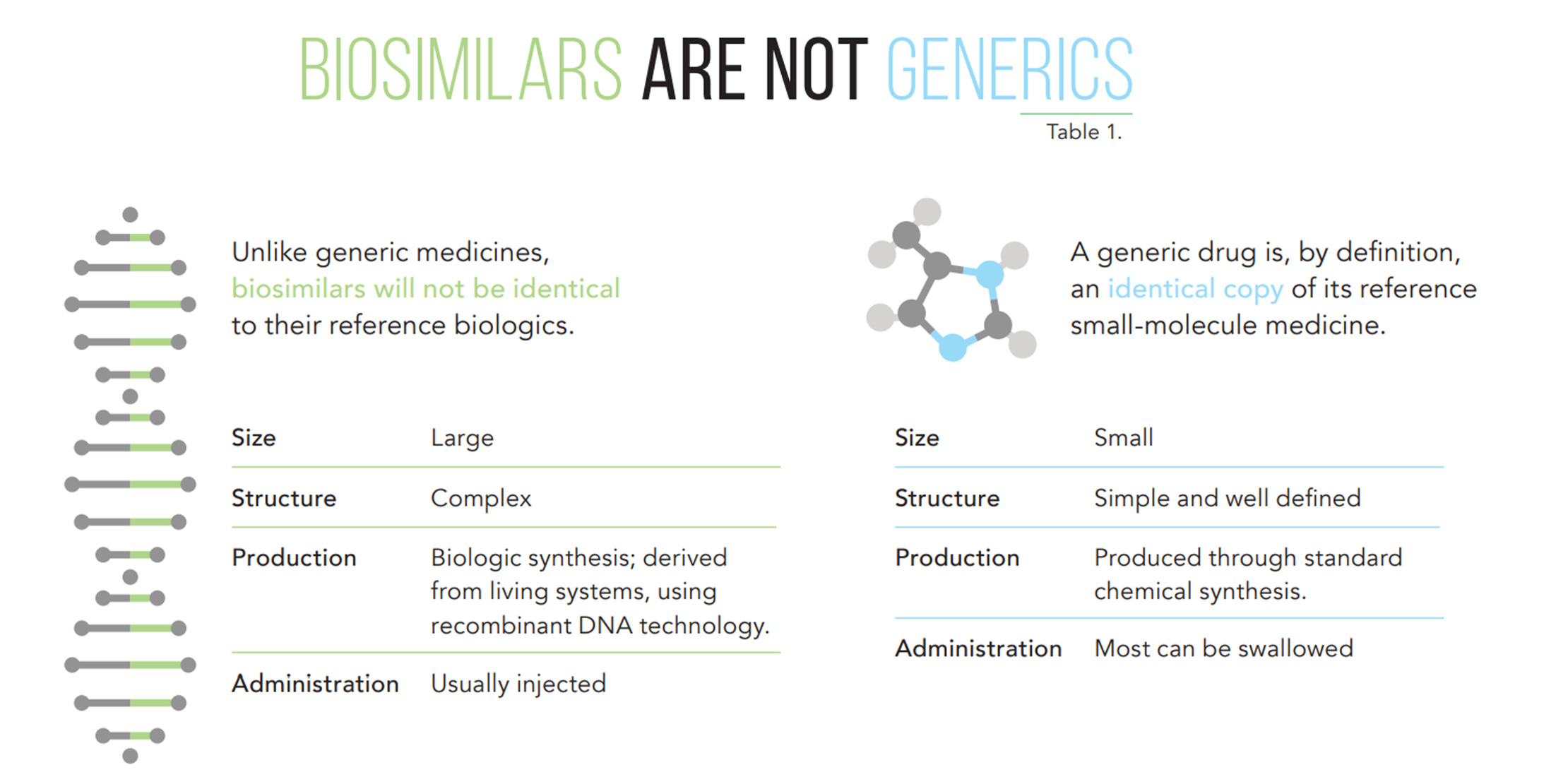
A biosimilar, or similar therapeutic product, is an extremely similar but not identical version of the original biotherapeutic, also known as a “reference.”
Many characteristics of biotherapeutic medicines are unique to and dependent on a specific manufacturing process. This is why biosimilar products are not identical copies.
The differences between the reference product and the intended copy must be understood, quantified, and sufficiently studied before a product achieves marketing authorization as a biosimilar.

Similarity between a biosimilar and its reference biotherapeutic product should be evaluated in all respects: quality, safety, and efficacy.
Copies of biotherapeutic medicines that have not undergone head-to-head comparisons with an appropriate reference product put patient safety at risk and should not be licensed via biosimilar pathways.
While there are inherent variations from batch to batch of a biotherapeutic, these differences are minor and tightly controlled by the manufacturing process within a certain range so quality is not affected.
This is not the same as differences between the original biologic and biosimilar. For this reason, terms such as “biogenerics” or “generic biologicals” are incorrect, simply because it isn’t possible to directly recreate the same molecule.
The challenges of regulating biosimilars

Pharmacy-mediated substitution for biosimilars
This position paper from IFPMA addresses substitution relating to biosimilars and their reference products at the retail pharmacy level. While this practice has been in place in many countries for generics, for biosimilars, the practice is only emerging.
Read moreGuidelines on evaluation of biosimilars
The WHO published its Guidelines on evaluation of biosimilars in 2022.
Its purpose is to provide an international norm for evaluating biosimilars with a high degree of similarity with an already licensed, reference biotherapeutic medicine.
The implementation of this guideline is an ongoing process in many countries, and IFPMA is committed to working with all stakeholders to support science-based legal and regulatory frameworks at the national level.
Cell and gene therapies
Cell and gene therapies, along with tissue engineering techniques, come under the umbrella of regenerative medicine or advanced therapies (advanced therapy medicinal products or ATMPs).
Gene therapy is the transfer of genetic material to a patient to treat a disease. It’s a promising treatment option for diseases including inherited disorders, some cancers, and rare genetic disorders.
Cell therapy aims to treat diseases by restoring or altering certain sets of cells or by using cells to carry a therapy through the body. These innovative treatments can help reduce or eliminate the need for treatments that need to be taken continuously, often for life.
Regulatory complexities
Advanced therapies raise regulatory complexities different from those found in more traditional pharmaceutical technologies.
Important differences exist in the regulation, definition, scope, and approval of cell and gene therapy products by regulatory authorities around the world.
There are only a few regions in the world where a regulatory framework exists for advanced therapy medicinal products. This may cause uncertainty when it comes to requirements needed for regulatory approval and subsequent regulatory processes, which can ultimately lead to delays in patient access.
Differences in therapy classification, orphan drug designation, review procedures, and indications of use could result in differences in clinical practice in different countries.
Cell and gene therapies present significant challenges for regulatory authorities, manufacturers, developers, health care providers, and patients involved in their application.

Convergence and reliance approaches for advanced therapy medicinal products
Cell, tissue and gene therapies offer significant potential to treat diseases with high unmet medical needs, and consist of human cell and tissue products for medical use and advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs). IFPMA shares points to consider when promoting regulatory convergence and reliance approaches for ATMPs.
Read moreJoin the global effort to help convergence
IFPMA invites all stakeholders to join a global effort to develop a set of common principles that can help convergence in the regulatory evaluation and market availability of advanced therapy medicinal products.