Vaccines


With every vaccine, vaccine developers and manufacturers, together with partners in the global health community, do more than improve and save lives. They enable vaccination that strengthens global health security through resilient and sustainable national immunization programs around the world. These help people during childhood and beyond while communities, and nations thrive.
Overview
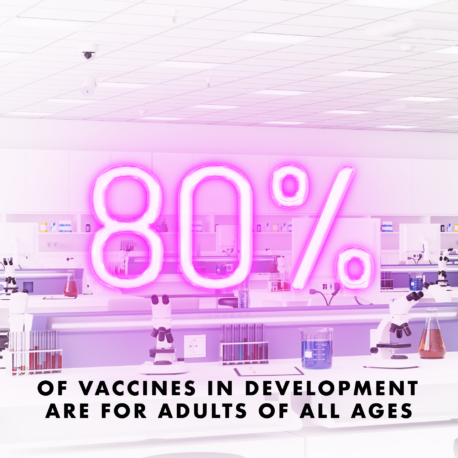
When it comes to vaccines, companies contribute to R&D, manufacturing, supply, and health system strengthening while constantly innovating to help transform the health of people of all ages.
They leverage their unique knowledge of vaccines from a scientific and regulatory perspective as well as deploying their in-depth understanding of vaccination best practices. In this way, they support authorities worldwide to anticipate emerging threats, develop innovative solutions, and share accurate, science-based information.
IFPMA and our members also build confidence in vaccination.
Through impactful partnerships, companies are building capacities and networks to support resilient and sustainable national immunization programs around the world.
Looking to the future, we and our industry are committed to the vision and goals of the Immunization Agenda 2030. That is, to help “achieve through a collective endeavor by all stakeholders a world where everyone, everywhere, at every age, fully benefits from vaccines for good health and well-being.”

Vaccine innovation
New vaccines are constantly being discovered and developed. Existing vaccines are continuously being improved. Novel approaches to producing, storing, and administrating vaccines are being put in place.
This vaccine innovation happens because universities, research institutions, biotechs, and the innovative pharmaceutical industry are dedicated to science, scientific ingenuity, and sustained investment.
Bridging the gap between breakthrough discoveries and revolutionary vaccines, companies are uniquely placed to share the benefits of scientific innovation with communities worldwide.

Pathogen sharing
Immediate, unrestricted access to pathogens and their genetic information is fundamental to global health security and the crucial first step to developing the vaccines, medicines, and tests the world needs.
Vaccines today
Vaccines currently protect against 30 different infectious diseases. They help to prevent certain infections, such as Human Papillomavirus, which can lead to cancers like cervical cancer, as well as Hepatitis B, which could trigger liver cancer.
Recently launched vaccines include those that help protect against meningococcal diseases, Ebola, malaria, COVID-19, and HPV-related cancers including cervical cancer.
Companies have developed a promising pipeline that includes vaccines for tuberculosis, multivalent meningitis, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). This sustained vaccine innovation lies at the heart of our partnerships, such as with Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, COVAX, and the Access to COVID-19 Tools (ACT) Accelerator.
Increasing protection against more diseases and disease strains. Creating new formulations. Combining vaccines to make them more accessible. Exploring new technologies that help vaccines work better and offer longer protection. Developing vaccine technologies that make it easier to scale up or rapidly pivot production to tackle new variants and other viruses with pandemic potential.
The innovative pharmaceutical industry is constantly at work.
To grow our collective impact over the next five years, companies commit to innovating new vaccine solutions. In addition, they aim to reach the most in need and underserved, support the strengthening of immunization services, prepare for public health emergencies, and partner to maximize impact. Working together, we can scale vaccine innovation through sustained immunization to make sure no one is left behind.
Developing new vaccines
There are currently nearly 260 vaccine candidates being developed through a range of technical platforms to protect against diseases and pathogens that lack effective vaccines.
Innovative pharmaceutical companies have helped launch new vaccines for COVID-19, HIV, Zika, Norovirus, Alzheimer’s disease, Lyme Disease, Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), dengue, and Group B streptococcus.
It’s important to remember that vaccine innovation can be a long, challenging process. It took 50 years of trial and error before Jonas Silk’s polio vaccine was introduced. A vaccine against HIV/AIDS is yet to be developed, 40 years after the virus appeared.
But, after more than 50 years researching, scientists have finally developed a malaria vaccine, the first for any parasitic disease, with what is being called “world-changing” potential.

The mRNA vaccines used against COVID-19 were the result of research dating back to the late 1970s.
Improving existing vaccines
Companies are working on improving existing vaccines so that they perform better for longer against diseases like meningitis, pneumonia, and flu.
They are also developing COVID-19 vaccines that can be given in one dose with others, such as with flu and pneumonia vaccines.
At the same time, they are improving how vaccines are made, distributed, and administered to improve access and affordability.
Our goal is to make sure the global community can tackle current and future threats and help eradicate, eliminate, or control infectious diseases.
Unlocking the value of vaccines
Vaccines help prevent and control outbreaks, tackle endemic and pandemic diseases, protect the health impacts of climate change, and lower health inequalities. They help improve the economies of lower-income countries.
Every year, vaccines prevent 4-5 million deaths in all age groups from diseases like diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whooping cough), influenza, and measles. If global vaccination coverage improved, an extra 1.5 million deaths could be avoided yearly.
Helping prevent and control outbreaks. Tackling endemic and pandemic diseases. Protecting the health impacts of climate change, and lowering health inequalities. Vaccines are playing a crucial role in achieving 14 out of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
deaths prevented in children under 5 in low-and middle-income countries in the last 20 years
lives are saved per minute by vaccines in LMICs
deaths prevented in this decade alone

The socio-economic value of adult immunisation programmes
This “first-of-its kind” report by the Office of Health Economics, an independent health economics research organisation, investigates the health and socio-economic benefits of adult vaccination programs.
The economic benefits of vaccines
Ultimately, vaccines improve financial security for society. This can lead to greater investment and improved political and economic stability.
Between 2016 and 2030, vaccines will help prevent 24 million people in some of the world’s poorest countries from slipping into poverty, by allowing families to avoid the often-heavy healthcare costs that infectious diseases can bring.
On top of these savings made on medical costs, when the value of a life saved is included, the return on investment rises to USD 51 per dollar invested in immunization.

Improved life prospects
Vaccinated children are less likely to have long-term vaccine-preventable disabilities and are more likely to go to school, leading to improved education, better life prospects, and higher future earnings.

Higher workplace productivity
When adults are vaccinated, they are less likely to miss work because of illness and there’s a greater chance of them actively contributing to society for longer.

Supports gender equality
If women and children are vaccinated, it supports gender equality. Women can access health services without the burden of female-specific disease or caring for sick children.

#VaccinesForLife: Vaccines, Lighting up our future
Investing in adult vaccination programs can help protect lives, our healthcare systems, and our economies.
#VaccinesForLife - Lighting Up A Healthier Future

#TeamVaccines #VaccinesForLife
Vaccines are helping people of all ages avoid dangerous infections, protecting communities from fast-spreading outbreaks and helping to keep us from losing those we love.
Implementing a life-course approach to immunization
The life-course approach recognizes the role of vaccination as a strategy to prevent diseases and maximize health over a person’s entire life, regardless of age.
Policies that support immunization across the life-course have many benefits, including individual and population health, health system resilience and sustainability, and economic prosperity.
IFPMA calls on global and regional stakeholders and governments to strengthen pandemic preparedness and responsiveness by taking a life-course immunization approach. This will expand access to vaccines, improve uptake, and ensure optimal protection of all populations.
Seasonal influenza
Together with the global health community, the innovative pharmaceutical industry is committed to improving seasonal influenza vaccine coverage and working towards influenza pandemic preparedness for the future.

Life-course immunization: Country landscape report
Immunization is the greatest success story of the twentieth century. Vaccines eliminated most of the childhood diseases that used to cause millions of deaths, making possible a life without disabilities caused by certain communicable diseases like polio for the first time in human history.
Read moreAntimicrobial resistance and the role of vaccines
Vaccines prevent commonly acquired bacterial infections, whose treatment would require antimicrobial medicines, reducing the opportunity for bacteria to develop resistance.
For instance, after the Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) conjugate vaccine was recommended for use in Canada in 1988, cases of Hib disease dropped by 97% from 1986 to 2017.
There are 124 Vaccines that can prevent viral infections, often treated inappropriately with antibiotics, which can give rise to secondary infections that require antibiotic treatment.
A compelling and growing evidence base demonstrates that vaccines are also a critical complementary tool to mitigate the threat of AMR. To maintain the effectiveness of antibiotics over an extended period of time, we need to not only ensure appropriate use of antibiotics, but as part of coordinated stewardship plan, maximize the impact of vaccination on AMR.
Vaccines can prevent community-acquired bacterial infections, which can curb the spread of resistance and also reduces antibiotic consumption. Vaccines against certain viral disease like influenza can also help reduce opportunities for inappropriate antibiotic use, and can further prevent secondary bacterial infections in susceptible patients which would need to be treated with antibiotics.
Leveraging the potential of vaccines against AMR

Access and uptake
Increase the uptake of licensed, AMR-relevant vaccines to prevent disease and reduce demand for antibiotics.

Research and development
Enable a market that supports development of new AMR-relevant vaccines for pathogens that pose a threat to human health, especially for those resistant to antimicrobials. This includes changes to how these vaccines are assessed, recommended, and reimbursed.

Data for impact
Expand the evidence on the impact and value of vaccines on AMR to guide decision-making and vaccine development, including the health economic case to establish their value proposition.

Antimicrobial resistance
IFPMA helps lead the innovative pharmaceutical industry’s work on antimicrobial resistance (AMR). We raise awareness of the unique challenges in combating AMR and of measures that could establish economic conditions favorable to long-term investment into antibiotic R&D.
Maintaining and growing confidence in vaccination
The innovative pharmaceutical industry plays a vital role in maintaining and growing confidence in vaccination by researching, developing, and communicating around vaccines with demonstrated safety and efficacy profiles.
Maintaining and growing confidence in vaccination is an urgent public health issue. It’s vital to prevent the spread of disease and restore vaccination coverage rates to continue to protect and enhance health and well-being, while contributing to national development and prosperity.
Despite the widespread availability of many vaccines with demonstrated safety and efficacy profiles, we continue to see outbreaks, disability, and deaths from vaccine-preventable diseases including measles, polio, and influenza. We will only be successful when people are willing to be vaccinated.
Through coordinated action by all stakeholders and a focus on building resilient immunization programs, routine vaccination can continue to protect millions of lives every year.
As key partners in global health, IFPMA and our members play an essential role in building and sustaining confidence by developing high quality, safe, effective vaccines that meet some of the world’s most challenging health needs.
COVID-19 and the future of vaccines
The COVID-19 pandemic has given us a clear vision of what has to happen regarding vaccination for the future.
We need coordinated action at local, national, regional, and global levels to build and sustain confidence in vaccines while making sure resilient immunization programs are in place.
Vaccine hesitancy and the complex factors that cause it must be understood and addressed by the entire global health community to boost vaccine confidence worldwide.
Sustaining confidence in vaccines
Through impactful partnerships, member companies build capacities and networks to support resilient and sustainable national immunization programs around the world. Together, they communicate and collaborate to maintain and grow confidence in vaccination.
Member companies support:
of countries identified vaccine hesitancy as an evolving threat to their immunization programs
in 2019, WHO identified vaccine hesitancy as it’s 8th largest global health threat
deaths per year are prevented by immunization
Partnering for universal immunization
Together with our partners, we and our members are determined to grow the vaccinated community until universal immunization is achieved.
Innovative pharmaceutical companies make a unique and vital contribution. They develop new and improved vaccines, scale up supply, provide a reliable supply of quality and effective vaccines, and help make sure vaccines reach the communities who need them most.
They have developed business models that enable them to invest to ensure vaccines can be produced and supplied reliably today and improved vaccines and new technologies developed for tomorrow.
Partner spotlight: Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance
Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, was created as a public-private partnership with the help of IFPMA member companies. IFPMA representatives have one seat on the Gavi Board and one on the Gavi Program Policy Committee.
The benefits of this partnership when it comes to scaling vaccine innovation and supply are clear.
Gavi provides aggregated demand and secured financing for the purchase of vaccines. This enables IFPMA’s innovative pharmaceutical member companies to scale-up vaccine manufacturing capacity to deliver the volumes required.
Our member companies’ work with Gavi has not just resulted in the production of life-saving vaccines. It has increased access to them.
Today, IFPMA members’ engagement with Gavi extends beyond vaccine development, testing, production, storage, distribution, and building manufacturing capacity in the global south. It supports national procurement and makes sure health systems have the capacity to deliver and administer vaccines.
Additionally, companies offer training for healthcare workers and immunization managers.

Generation Gavi
IFPMA and our members are working with the Gavi Alliance to roll out the most comprehensive package of protection to the world’s poorest countries. Our aim is to vaccinate the remaining 20% of children around the world without access to new vaccines by 2030.
Follow #TeamVaccines
Read and share our #TeamVaccines stories to hear firsthand from those who work to make vaccines to help protect us all from infectious diseases.